What if Jira stories didn’t just describe work—but triggered it?
This is a real-world walkthrough of how a Jira user story was fetched via Atlassian MCP Server, assigned to GitHub Copilot Agent Mode, fully implemented, validated, and closed.
Why This Experiment Matters
Most AI demos stop at:
- Code suggestions
- Single file refactors
- Chat-based assistance
But real software delivery lives across systems:
- Jira for requirements
- GitHub for code
- CI for validation
This experiment asked a deeper question:
Can an AI agent read a Jira story from the source of truth, act on it responsibly, and close the feedback loop like a real engineer?
The Setup: Connecting Jira to Copilot Using Atlassian MCP Server
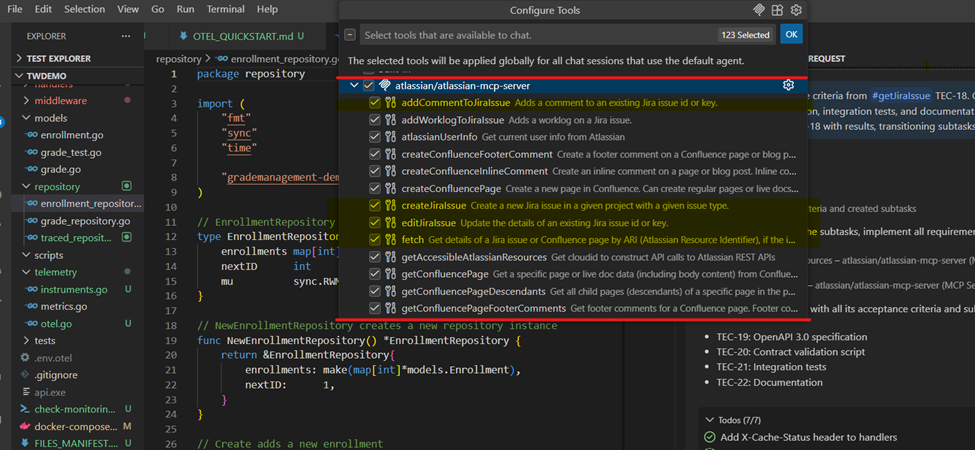
The enabler was Atlassian MCP Server.
What Role Does MCP Play?
Atlassian MCP Server acts as a secure, structured bridge between:
- Jira (issues, acceptance criteria, subtasks, transitions)
- GitHub Copilot Agent
Instead of pasting Jira text into prompts, Copilot could:
- Fetch the issue directly from Jira
- Read it in machine-structured form
- Update Jira programmatically with results
This makes the workflow auditable, scalable, and enterprise ready.
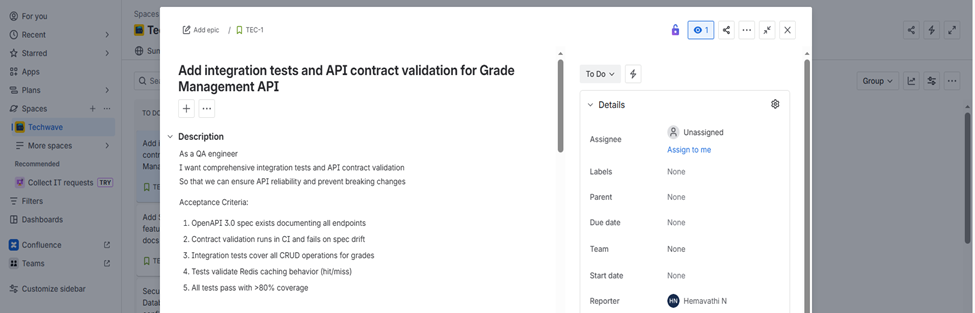
Step 1: Copilot Fetches the Jira Story via Atlassian MCP
The process started with a single instruction to the agent:

Read acceptance criteria from Jira issue TEC-1.
Using Atlassian MCP Server, Copilot:
- Retrieved the Jira issue
- Parsed:
- Description
- Acceptance criteria
At this point, Copilot had the same context a human engineer would read on Jira.
Step 2: Translating Acceptance Criteria into an Execution Plan
Before writing code, the agent paused and planned.
From the Jira acceptance criteria, Copilot derived four clear workstreams:
- OpenAPI 3.0 Specification
- Contract Validation Script
- Integration Tests
- Documentation
Using Atlassian MCP, Copilot:
- Created Jira subtasks
- Linked each subtask to a specific acceptance criterion
- Assigned clear ownership and scope
This step is critical: Good engineering starts with decomposition, not implementation.

Step 3: Autonomous Implementation
Once subtasks existed, Copilot executed them sequentially.
1. OpenAPI 3.0 Specification
- Generated a complete OpenAPI 3.0 spec
- Documented all Grade Management endpoints
- Included schemas, error responses, and headers
- Explicitly defined X-Cache-Status for cache visibility
2. Contract Validation
Next, Copilot implemented a contract validation script that:
- Compares live API routes against the OpenAPI spec
- Fails CI on Missing endpoints, Incorrect HTTP methods & Spec drift
This turned the OpenAPI spec into a living contract, not static documentation.
3. Integration Tests
Copilot then created comprehensive integration tests covering:
- CRUD Lifecycle
- Redis Cache Validation
Redis was provisioned via Docker, ensuring tests were CI-compatible.
Step 4: Validation, Coverage, and Quality Gates
Before touching Jira again, Copilot validated everything:
- Ran all integration tests
- Verified Redis behavior
- Ensured contract validation passed
- Confirmed test coverage exceeded 80%
Only after all quality gates passed did the agent proceed.

This is an important distinction:
The task wasn’t “done” because code existed—it was done because evidence existed.
Step 5: Closing the Loop Back in Jira
Using Atlassian MCP Server, Copilot:
- Posted a detailed comment on the Jira story explaining:
- What was implemented
- What was validated
- How to verify locally
- Transitioned each subtask to Done
- Updated the parent story status accordingly


This workflow demonstrates a shift from:
AI as an assistant to
AI as a delivery agent with guardrails
Key Takeaways
- Atlassian MCP enables system-level context, not copy-paste prompts
- Copilot Agent Mode can:
- Read requirements
- Plan work
- Implement responsibly
- Validate quality
- Close feedback loops
Final Reflection
Can AI write production code?
This experiment answers a more important question:
Can AI behave like a disciplined engineer inside real enterprise workflows?
With Jira as the source of truth, Atlassian MCP as the bridge, and GitHub Copilot as the agent
the answer is yes. And this is only the beginning.
