Infrastructure as Code (IaC) has transformed how we manage cloud environments, with Terraform historically leading the charge. But as the licensing model of Terraform shifted away from fully open-source, the DevOps community responded — decisively and collaboratively.
Enter OpenTofu: a community-driven, fully open-source fork of Terraform, governed by the Linux Foundation and built for long-term stability, transparency, and innovation.
What is OpenTofu?
OpenTofu is a drop-in replacement for Terraform — maintaining full compatibility with existing Terraform configuration files while remaining true to open-source principles. It empowers organizations to manage infrastructure with confidence, free from licensing concerns or vendor lock-in.
Whether you’re managing a few EC2 instances or orchestrating multi-region Kubernetes clusters, OpenTofu offers the same reliability and developer experience, backed by a growing community and open governance.
Why OpenTofu?
1. Drop-in Replacement
OpenTofu speaks the same language as Terraform — HCL (HashiCorp Configuration Language). Your existing .tf files and modules will work without modification, enabling a frictionless transition.
2. Truly Open Source
Licensed under MPL-2.0, OpenTofu eliminates concerns about restrictive licensing or usage limitations — especially critical for teams integrating IaC into commercial platforms or managed services.
3. Security-First Features
OpenTofu includes built-in state encryption, with even more enhancements planned based on real-world community needs. This enables a more secure IaC practice — out of the box.
4. Zero Learning Curve
The CLI, syntax, commands, and workflow are identical to Terraform. If you’re familiar with Terraform, you already know how to use OpenTofu. No new training or onboarding is required.
OpenTofu in Action
I recently deployed a production-grade AWS environment using OpenTofu — without a single change to existing configuration:
- 1.VPC and Subnet Setup
- 2.Internet Gateway and Route Tables
- 3.Security Groups and IAM Roles
- 4.EC2 Instance Provisioning
- 5.S3 Bucket Integration
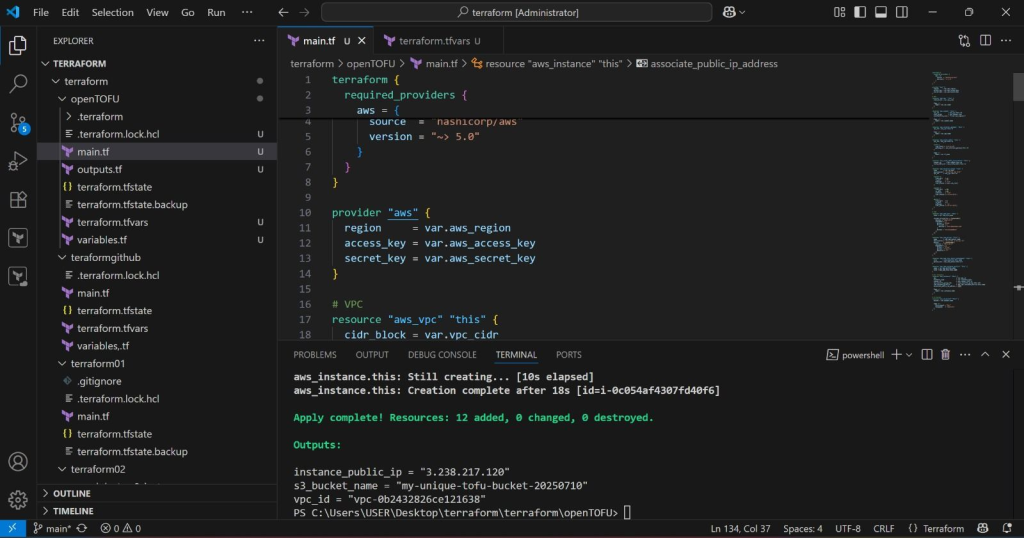
This success validated OpenTofu’s promise seamless compatibility with Terraform configurations and reliable infrastructure provisioning — all within an open governance model.
Getting Started with OpenTofu
1.Install OpenTofu
Depending on your operating system, you can install OpenTofu using a package manager:
winget install --exact --id=OpenTofu.Tofu
Explanation:
This command uses winget to install the latest stable version of OpenTofu. Once installed, the tofu CLI becomes available on your terminal, just like terraform.
Alternative for Linux (manual install or script):
curl -sSfL https://get.opentofu.org/install.sh | sh2.Initialize a Project Directory
tofu init
Explanation:
This command sets up the working directory for OpenTofu. It:
- Downloads the required provider plugins (e.g., AWS, Azure).
- Sets up the .terraform directory structure.
- Ensures the configuration files (
main.tf,provider.tf, etc.) are validated.
It’s exactly the same as terraform init.
3.Preview the Infrastructure Plan
tofu plan
Explanation:
This command shows what changes OpenTofu will make to your infrastructure without actually applying them.
It performs a dry run and outputs:
- What resources will be created, updated, or destroyed.
- Differences between your desired config and real-world state.
4. Apply the Infrastructure Changes
tofu apply
Explanation:
This executes the plan and provisions or updates infrastructure as defined in your .tf files.
You’ll be prompted to confirm (yes) before changes are applied — ensuring safe and controlled deployments.
5.Optional: Replace Terraform CLI
If you’re fully transitioning from Terraform, you can alias the terraform command to use OpenTofu:
alias terraform='tofu'
Explanation:
This is helpful for CI/CD pipelines or scripts where replacing all instances of terraform would be tedious.
Note: Use this carefully in production scripts — test in dev/staging first.
6.Use State Encryption (Optional but Recommended)
OpenTofu supports built-in state encryption using a symmetric key:
terraform {
backend "local" {
path = "terraform.tfstate"
encryption {
key = "my-secret-password"
}
}
}
Explanation:
This encrypts the terraform.tfstate file on disk, adding a security layer especially useful in team or shared environments.
Final Thoughts
OpenTofu marks a significant shift in the Infrastructure as Code ecosystem — empowering teams with a truly open-source, community-governed, and fully compatible alternative to Terraform.
With no learning curve, seamless migration, and powerful features like built-in state encryption, OpenTofu is more than just a fork — it’s a future-proof choice for organizations that prioritize transparency, flexibility, and open innovation.
Whether you’re managing internal environments or integrating IaC into commercial platforms, OpenTofu offers the freedom and confidence your DevOps workflows need.
Embrace open infrastructure. Say goodbye to vendor lock-in. Say hello to OpenTofu.
